Agradecimiento a: http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=2105755
Preface:
11 cool OS X El Capitan tips to use today. In the same way, select the appropriate icon (for the shared Mac, AirPort Disk or Time Capsule volume), choose Connect As and enter your password. Manage your Wi-Fi network from your devices. With the AirPort Utility app on your iOS and iPadOS devices, you can set up and monitor your network from your devices as easily as you can from your Mac.
In past versions of Mac OS X, the built in backup tool, Time Machine was a lot less picky about where you back up your files to. You could even back up to a Samba file share if you enabled the «unsupported volumes» hack.
But that ended with Snow Leopard. Starting with the release of OSX 10.7 Lion, Apple started cinching down on where you could back up your system to, ostensibly for security reasons. Now, with Mac OS X 10.8 «Mountain Lion», it’s gotten to the point where essentially the only places you can back up your system using Time Machine are either on another Mac OS X File Server or on an Apple Time Capsule. My assumption is that their intent is merely to bolster their hardware sales.
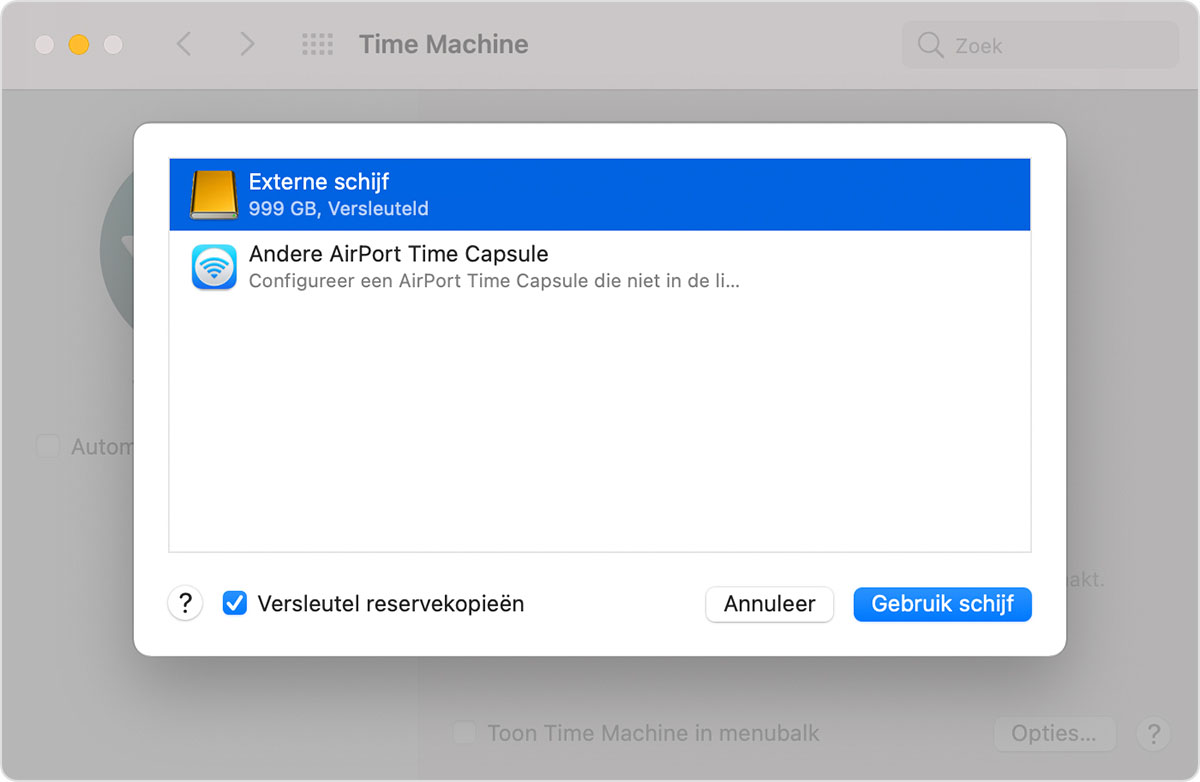
I don’t know too many people who stay exclusively within the «walled garden» for all their computing needs. Certainly people with a lot more money to burn than me. But for a much more economical approach than shelling out around $300 for an over-glorified USB drive, you could just follow this guide to set up your Ubuntu file server to look and behave exactly like Time Machine would expect a real Time Capsule or Mac to.
Step 1: Install Netatalk
installing Netatalk, the open source Apple Filing Protocol (AFP) implementation is easy! The packages are already in the repos, which makes me wonder why it’s not enabled by default.
Install the following packages:
Step 2: Configure /etc/nsswitch.conf
Once those packages are installed, there are actually 4 configuration files that need to be edited in order for the Macs on your network to access your AFP shares properly.
locate the line that reads
and add ‘mdns’ to it so it now reads
press ctrl+o to save and ctrl+x to exit.
Step 3: /etc/avahi/services/afpd.service
paste the following code
NOTE: Just for fun you can change the string «<txt-record>model=TimeCapsule</txt-record>» to the following devices to change how they appear in Finder on OSX:
- MacBook
- Laptop
- MacBook4,1,Black
- MacBookPro
- MacBookAir
- MacPro
- iMac
- Macmini
- AppleTV
- iPhone
- iPodTouch
- iPad
- Xserve
- RackMac
- TimeCapsule
- PowerBook
- PowerMac
- AppleTV1
- AppleTV2
- AirPort
Type them exactly as I have typed them. They are case sensitive. If you type the model name in wrong, your AFP share will show up as a Cinema Display in Finder. There are actually dozens more. Too many to list actually, but if you’re interested you can find the name strings in /System/Library/CoreServices/CoreTypes.bundle/Contents/Info.plist
Step 4: /etc/netatalk/AppleVolumes.default
This is where you actually declare your shared file.
scroll down to the bottom and find the section that reads
change the path «~/» (which points to /home/username) to the directory you want to share. For me I created a separate partition mounted at /TimeCapsule.
IMPORTANT!!! You would be able to access the share from a Mac, but if you plan to use this share for Time Machine backup, you need to add ‘tm’ to options:upriv,usedots
like this:
press ctrl+o to save and ctrl+x to exit.
Step 5: /etc/default/netatalk
this is the last file that you need to edit. Edit with
find the section that looks like this
and edit it so it looks like this:
That is all. Now you can enjoy making incremental backups with Time Machine without the hassle of manually mounting disks. I actually did this on my Windows 8 HTPC/Mediaserver using a very stripped down headless Debian virtualbox installation that runs at boot as a background service and uses only 64MB of RAM and paravirtualized bridged ethernet.
Screenshot of my Mac backing up to the Debian virtual machine on my Windows 8 box.
Home » Prescription and Medication »There are many different ways to take medications orally. Capsules and tablets are generally the most common. Have you ever found yourself wondering how to take your newly prescribed medicine? If you have trouble swallowing them, then there is advice that can help you.
So, in this article, we will discuss everything about medicine capsules, whether you have to swallow them, and if there are other ways to take them. Before we get into all the details, here’s a quick summary.
Are you supposed to swallow capsules? Medication presented in capsule form is designed to be swallowed. Do not chew, break, crush, or open a capsule to pour out the medication, unless a healthcare professional has advised you to. Some pills may be harmful if crushed or opened. If in doubt seek professional medical guidance.
Let’s take a look at capsules in a little more depth below:
- What is a capsule?
- Are you supposed to swallow capsules?
- The differences between a capsule and a tablet
- Are tablets or capsules easier to swallow?
- What is a capsule cover made of?
- Can you open a capsule?
- How long does a capsule take to dissolve in your body?
What Is a Capsule?
In the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, a capsule or ‘encapsulation’ refers to a range of techniques used to enclose medicine. The outside shell is more commonly known as a ‘capsule’. They can be taken orally or as a suppository.
Below, we are going to take a look at the differences between capsules and tablets.
The Difference Between Capsules and Tablets
Sometimes your prescribed medications may be in the form of capsules and/or tablets. A tablet is usually in the form of flat tablets and a capsule is almost cylindrical.
Tablets can be cut into two, whereas capsules cannot be cut into two. A capsule consists of powder or jelly enclosed in a dissolvable gelatin container. A tablet is a compressed powder in solid form.
Tablets are often coated with sugar or similar substances, which means that the drug contained in it will not immediately enter the blood-stream. But, the drug in the capsules is known to enter the blood-stream immediately – as soon as the capsule dissolves.
Tablets are known to be less expensive when compared to capsules. They’re manufactured by compressing and packing the materials using force. Tablets are also known to have more shelf life and retain their potential for a longer period than the capsules. Moreover, tablets are available in different sizes and shapes.
The only drawback that can be seen with tablets is that large tablets can be hard to swallow. The only way to to take a larger tablet, if you have trouble swallowing, is to break it or crush it to powder.
Be sure you always consult with your doctor or medical professional before breaking or crushing a tablet.
Tablets Versus Capsules
Let’s take a look at the main differences between a tablet and a capsule – and their pro’s and cons.
- A capsule consists of powder or jelly enclosed in a dissolvable plastic container. A tablet is a compressed powder in solid form.
- Tablets can be cut into two, whereas capsules cannot.
- Tablets are coated with sugar or similar substances, which means the drug contained in them will not immediately enter the blood-stream. But, the drug in the capsule is known to enter the blood-stream immediately.
- Tablets are also known to have more shelf life and also retain their potential for a longer period than capsules.
- Tablets are available in different sizes and shapes. Capsules have fewer options on size or shape.
- Tablets are known to be less expensive when compared to capsules.
- When compared to tablets, capsules are easy to swallow.
Which leads perfectly on to swallowing capsules and/or tablets…
Are Tablets or Capsules Easier to Swallow?
The physical properties of the coating on a softgel capsule result with them ‘floating in the mouth’ when taken with water. As a result, the swallowing of capsules can often be difficult for some people.
What Do I Do If I Have Problems Swallowing Capsules?
In patients who experience such difficulty, it is suggested that they try leaning forward when swallowing, as this has been found to assist. It may be necessary to reassure patients about this technique as they may initially find it unnatural to execute.
Capsules Can Be More Difficult to Swallow Than Tablets
Many patients have difficulties, both psychologically and physically, swallowing medications. The swallowing of capsules can be particularly difficult. This is because capsules are lighter than water and float due to air trapped inside the gelatine shell.
What Do I Do If I Have Problems Swallowing Tablets?
In comparison, tablets are heavier than water and do not float. The usual method of swallowing tablets is to place them on the tongue, filling the mouth with water, tilting the head back and swallowing. This works well for tablets because they don’t float and when the head is tilted back, gravity helps the tablet to be swallowed more easily.
If you tilt your head back and use the same technique as for swallowing tablets when you are trying to swallow a capsule, it will float on the water in the front of the mouth, making it harder to swallow.
Most capsules are intended to be swallowed whole so the ‘lean-forward’ technique should help you. If swallowing difficulties remain, talk to your doctor or health professional about other options.
Are Capsule Covers Made of Plastic?
You’re probably not alone if you’re wondering if capsule covers are made of plastic. It is quite easy to think this as the shells do indeed give the impression they’re made of plastic. The answer to this question is no, the capsule shell is not made of plastic.
Capsule shells are made of bio-degradable material extracted from animals and plants. There are two types of shells for capsules. Both capsule shells are made either from animal or plant extracts or their derivatives.
Capsule shells are made of biodegradable material extracted from animals and plants.
What Is a Capsule Cover Made of Exactly?
Capsule Fight Mac Os X
There are various different types of capsules, all with different shells. Many shells are made from gelatin.
This is because gelatin is a natural, safe, non-allergenic, clean, and economical ingredient. There are other types of shells made of potato starch, a vegetarian shell made from tapioca, and some from fish gelatin.
- Gelatin
- Potato Starch
- Tapioca (v)
- Fish Gelatin
The type of shell on your capsule will depend on the type of drug you’ve been prescribed. The most common types are made out of either hard gelatin or soft gelatin. Soft gelatin capsules are more often used when your medicine is of a liquid variety.
Let’s take a look below at the most common types of capsules.
Hard Gelatin Capsule
The shell of hard gelatin capsules contains 13–16% water. Storage of hard-gelatin capsules at very low humidity can cause them to turn brittle and If stored at high humidity, the capsules become flaccid. This is why they are usually presented in packaging material such as aluminum strip packing, or foil. The foil protects the hard-shelled capsule from moisture.
Soft Gelatin Capsule
Soft gelatin capsules have soft, globular, gelatin shells somewhat thicker than that of hard gelatin capsules. The gelation is plasticized by the addition of glycerin and other elements to create the softshell. It also may contain a preservative to prevent any fungal growth.
Fish Gelatin
Capsule Fight Mac Os Catalina
Fish gelatin capsules are preferred for filling marine supplements such as fish oil.
Starch Capsules
A variety of soft capsules, called VegaGels, are 100% plant-based and contain only starch and lipids with no synthetic additives. Potato starch is the main ingredient of the transparent, smooth, flexible film, which can be shaped, filled, and packaged just like gelatin.
Is a Capsule Cover Harmful?
It is safe to swallow capsule covers. In general, the safer option is gelatin because the end product resembles its source far more than vegetarian capsules, and it’s not as chemically processed throughout.
Can You Open a Capsule Pill
It’s not advisable to open a capsule pill unless you’re advised to do so by a doctor or other medical professional. They may need to be swallowed whole because:
- They’re designed to release medicine slowly into your body over time and crushing them could cause an overdose
- Your stomach acid could stop them from working without their special coating
- They could be harmful to the lining of your stomach without their special coating
- They may taste unpleasant without their special coating
- You could get side effects from inhaling the powder from the crushed medicines
If you’ve been advised to open your capsule pill for any reason, the prescribing healthcare provider will tell you how to do this.
How Long Does It Take a Capsule to Dissolve in The Body?
According to The Orlando Clinical Research center, it takes approximately 30 minutes for a capsule to dissolve in the body.
In general, it typically takes approximately 30 minutes for most medications to dissolve. When a medication is coated in a special coating – which may help protect the drug from stomach acids – it may take longer to reach the bloodstream.
For example, aspirin may dissolve in a matter of minutes, while gelcaps may take much longer, due to their gel coating. These pills may also be easier to swallow, so it’s important to weigh the pros and cons of different medications.
When medications move through the human body, they encounter and are processed by different organs before finally being released into the bloodstream.
While this process may sound straightforward, different drugs dissolve at different rates, different formulas, and dosages breakdown differently – and each persons body metabolizes medication in their own unique speed and way.
Conclusion
We hope this article has been helpful to you. If you need help accessing your medications for an affordable price, get in touch with us or call 1-877-296-HOPE(4673) and speak to one of our representatives, we are always happy to help.
ENROLL NOWLEARN MORE